What is Net Income?
Net income is the amount of money that’s left after taxes and certain deductions are made from gross income.
Net income can also be called net profit, the bottom line, and net earnings.
Net Income for Businesses
Net income for a business represents the income remaining after subtracting the following from a company's total revenue:
All operating expenses
Cost of Goods Sold
Interest
Taxes
Preferred stock dividends (but not common stock dividends)
What Does Net Income Tell You About Businesses?
For businesses, net income indicates how well a company is managing its profit (i.e., earnings and expenses). Net income for a business is found on the income statement and is examined by shareholders, prospective investors, and potential lenders to help determine whether the company is solvent and able to pay additional debts.
Net Income for Individuals
For individuals, net income is defined more loosely and can refer to gross income net expenses (or your take-home pay).
For cash flow purposes, net income is the equivalent of net pay. This is the total amount you’ve earned during a pay period, minus the following deductions and taxes:
Social Security taxes
Medicare and Medicaid taxes
Health Insurance
Retirement contributions
Wage garnishments
Child support
What Deductions Can I Make to Find My Net Income?
All deductions may not apply to you and tax obligations may differ. For example, your company may not provide a retirement contribution plan. Also note that net income can fluctuate from a tax perspective depending on which type of retirement plan you contribute to.
Where to Find Net Profit on the Income Statement
Net income is found on the last line of the income statement, which is why it’s often referred to as “the bottom line.” Depending on your country, you may also hear net income referred to as net profit or net earnings.
Net Income vs Gross Income
A company or individual’s net income will always be a smaller amount than its gross income (the income before taxes or adjustments).
Gross profit is located near the top of the income statement. It does not include all the company's fixed operating costs such as salaries, rent, amortization, deprecation, and other expenses that are all included in the company's net income.
For Businesses
Net income shows a company's income after all expenses. Gross profit shows a company's revenue minus the costs of sales/costs of goods sold. After product costs, the remaining income should cover all other expenses.
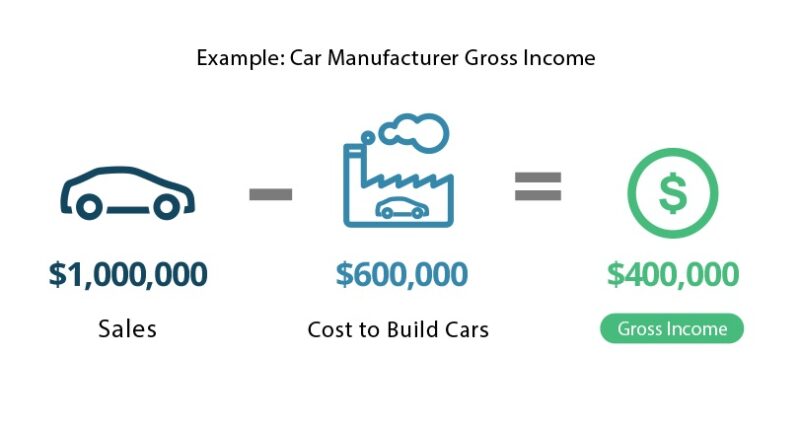
Example of Net Income vs Gross Profit
For example, a car manufacturer sells $1,000,000 worth of cars to dealerships. It costs $600,000 to build the cars (direct cost of sales) so the manufacturer's gross profit would therefore be $400,000.
For Individuals
Gross income for an individual is the total amount earned for a period of time before payroll deductions. In other words, net income is your net pay and usually the amount deposited into your own checking account.
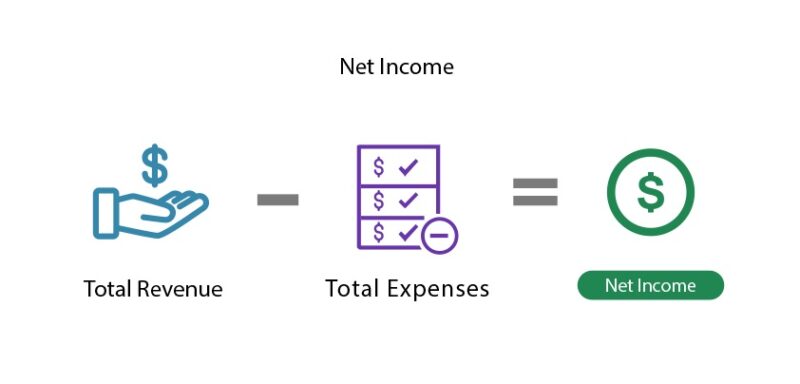
Net Income Formula
If you need to calculate net income for a business, use the following formula:
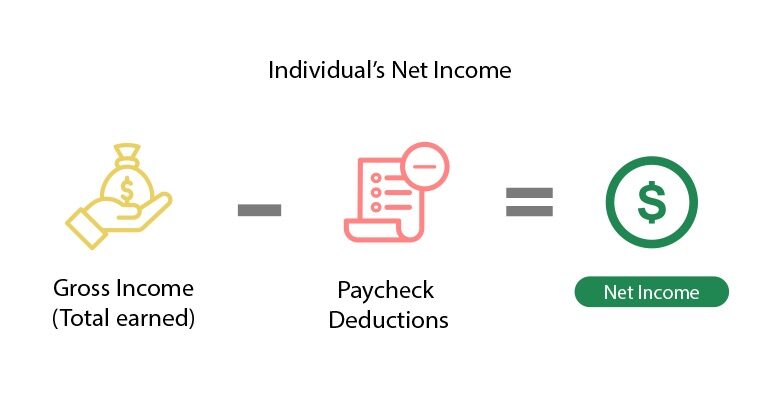
To calculate an individual’s net income, use the following formula (based on a recent pay stub):
Types of Net Income and Examples
Net income shows an individual’s or company’s financial position. When examining a company’s (or your own) finances, you can use net income in a variety of ways.
Two common types of net income examples include:
1. Calculating Annual Net Income for a Business
It is common to use annual net income and review it for growth over multiple years. Quarterly net income is scrutinized as public companies release earnings reports each financial quarter, with net income at the bottom of the income statement.
Example of Calculating Annual Net Income
Let's look at a hypothetical income statement for Company XYZ:
Company XYZ's Annual Income Statement
| Revenue | $2,000,000 |
| Operating Expenses: | |
| Salaries | ($1,000,000) |
| Rent | ($500,000) |
| Amortization | ($25,000) |
| Depreciation | ($75,000) |
| Operating Income | $400,000 |
| Interest Expense | ($50,000) |
| Tax | ($100,000) |
| Net Income | $250,000 |
To find net income using this formula, start with the firm's revenue then subtract all the expenses (e.g. salaries, rent, amortization, depreciation, interest expense, tax).
By using the formula we can see that:
Net Income = $2,000,000 - ($1,000,000 + $500,000 + $25,000 + $75,000 + $50,000 + $100,000) = $250,000
After taking the company's $2 million in revenue – and subtracting the $1,750,000 in total expenses it had over the year – Company Y was left with a net income of $250,000.
2. How to Calculate Operating Income
Operating income is found only by accounting for certain expenses, while net income accounts for all expenses. They both represent income earned by a company, but provide insight into the way money is managed at different points of operations.
Net operating income = Revenue - Operating expenses- Depreciation- Amortization
Net Income Interpretation: What to Know
The net operating income doesn’t account for company debt (interests paid) as net income does. It’s possible to have a profitable business but have debt wipe out that profit and show a negative net income.
Where Is Net Income on my Tax Form?
When filing your US taxes, you’ll report your gross income (total income) using a Form 1040.
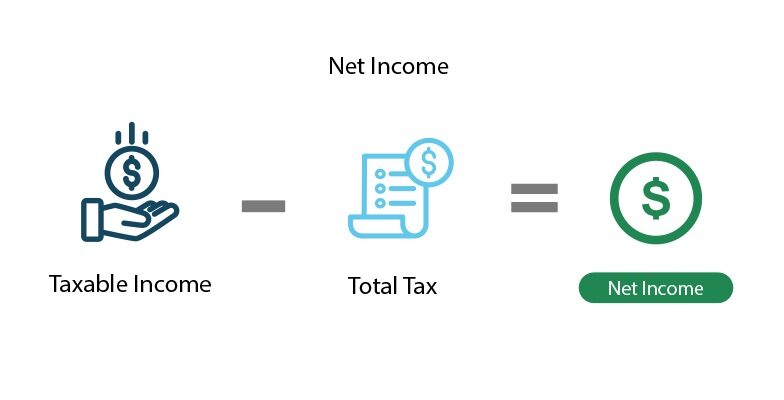
Since net income isn't a tax term, you won’t find it on your Form 1040. Instead, the Individual Income Tax Return determines an individual's adjusted gross income and taxable income. If you want to know your net income using a past tax return, use the following calculation:
Taxable Income - Total Tax = Net Income
Learn More About Net Income with InvestingAnswers
Need more answers on net income? Check out these definitions and articles from InvestingAnswers:
8 Key Facts to Know About a Company Before You Invest -- See how net income and other key terms can tell you whether or not to invest in a company.
Financial Statement Analysis: The Income Statement -- Learn the most important components of the income statement and how to use them to determine a company's profitability.




