What Is a Fiscal Quarter?
Fiscal quarters are consecutive, three-month periods within a company’s fiscal year (also referred to as a financial year). Fiscal quarters are used by publicly-traded companies to schedule the release of financial reports and the payment of stock dividends.
What’s the Difference Between Calendar Quarters and Fiscal Quarters?
Calendar quarters correspond to the standard calendar year. This means that the first quarter always begins with January 1st and the fourth quarter ends with December 31st.
Fiscal quarters coincide with a company's fiscal year – and they don't always align with a calendar year.
When Are Fiscal Quarter Dates?
The following fiscal quarter periods apply to companies whose fiscal year aligns with a regular calendar year:
2020 Fiscal Quarters
Q1 2020 Dates: January 1 - March 31
Q2 2020 Dates: April 1 - June 30
Q3 2020 Dates: July 1 - September 30
Q4 2020 Dates: October 1 - December 31
2021 Fiscal Quarters
Q1 2021 Dates: January 1 - March 31
Q2 2021 Dates: April 1 - June 30
Q3 2021 Dates: July 1 - September 30
Q4 2021 Dates: October 1 - December 31
2022 Fiscal Quarters
Q1 2022 Dates: January 1 - March 31
Q2 2022 Dates: April 1 - June 30
Q3 2022 Dates: July 1 - September 30
Q4 2022 Dates: October 1 - December 31
What Are Non-Standard Fiscal Quarters?
If a company’s fiscal quarters don’t align with regular fiscal calendar years (shown above), it has non-standard fiscal quarters.
Non-standard fiscal quarters are common for companies with highly seasonal revenue streams. For example, a children’s toy company may generate over half of its net revenue during Q4.
Example of Non-Standard Fiscal Quarters
Apple’s fiscal quarters cover the following months:
Q1: October, November, December
Q2: January, February, March
Q3: April, May, June
Q4: July, August, September
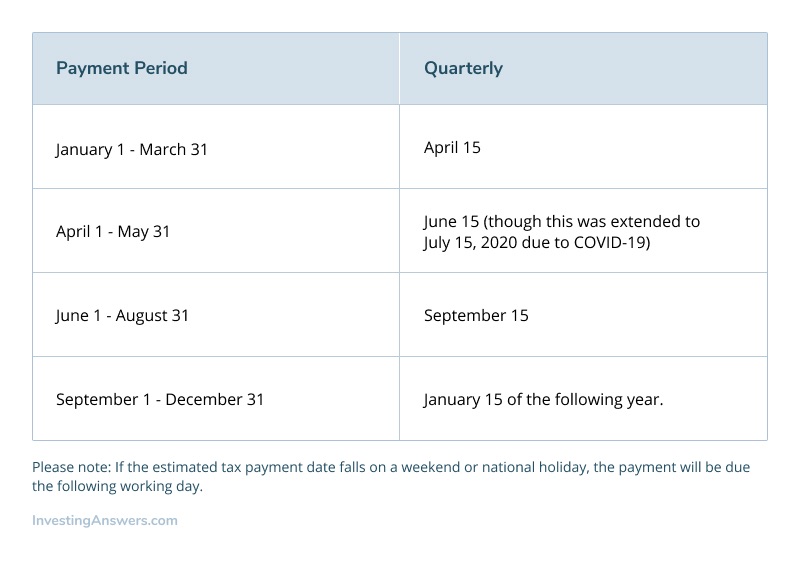
Quarterly Estimated Tax Payment Due Dates
For self-employed individuals (or those required to pay quarterly estimated taxes), it’s important to pay on time to avoid penalties. April 15 is the due date for filing tax returns, but you'll still need to make quarterly payments throughout the year. For traditional quarterly tax due dates, review the chart below:
Why Are Fiscal Quarters Important?
Publicly-traded companies issue reports at the end of each quarter which contain a set of financial statements that outline their financial information for that period. This allowws companies to track performance and make comparisons – but they're also used for tax purposes.
In the US, corporate quarterly reports (also called 10-Q reports) are filed through the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Should Private Companies Release Reports Each Fiscal Quarter?
Many privately-held corporations adhere to the fiscal year calendar and compile financial results on a quarterly basis. They aren’t required to release quarterly reports nor is this data typically required to be made public.
Where Do I Find Quarterly Reports?
Quarterly reports are often found on company websites or financial publications, but the most reliable source is the SEC's EDGAR system.
Pros of Quarterly Reports
In the United States, the model for publishing quarterly financial reports has been in place since the 1930s. There are obviously many advantages of quarterly reports:
Transparency
Quarterly reports give the public a look into the financials and performance of a company, providing valuable data on its financial well being.
Accountability
Since companies’ financial reports are made public and filed through the SEC, companies are held accountable for their performance and reporting. These reports also provide an incentive for companies to maximize performance in order to achieve self-imposed targets.
Valuation
Quarterly reports assist in creating market valuations of companies that can help attract capital.
Analysis
The data presented in quarterly reports allows companies to track performance, identify trends, and make important decisions about the future.
Comparison
Quarterly reports allow companies to compare their financials from previous periods or even with other companies in the same industry.
Dividends
Breaking the fiscal year into quarters allows companies to pay quarterly dividends, which can provide a steady stream of cash for shareholders.
Consistency
Since companies may operate on different calendars, quarters and quarterly reports provide consistency when making comparisons or tracking performance.
Cons of Quarterly Reports
Just like many concepts in finance, however, there are multiple drawbacks of quarterly reports:
Projections
Companies often include forward-looking statements which project results that have yet to be delivered. Investors who act on this information may be disappointed the next quarter. This could lead to investors selling stock, adding to overall market volatility.
Short-term
Investor Warren Buffett and banking CEO, Jamie Dimon are famous vocal critics of quarterly reporting. Their primary complaint is that instead of focusing on long-term growth (which is in the better interest of shareholders), strict adherence to quarterly results puts unnecessary pressure on short-term results.
Pressure
Analysts and investors rely on quarterly reports, so companies may be pressured to manage their numbers to meet their expectations.
Costly
It costs time and money to create financial reports, especially when they are required four times per year. This limitation could also deter private companies from going public.
No Context
While quarterly reporting provides the public with more data and transparency, it only offers an overview for a very limited period. Without additional context, investors may be discouraged to invest if they see undesirable results or less profitable quarters.




