What Are Assets?
The easiest way to define an asset is that it’s an economic resource that can be owned by an individual, company, or country. Assets are expected to provide future economic benefits like:
Increased value for a company or country
Increased net worth for an individual
Assets accomplish this by providing cash flow, reducing expenses, and/or increasing sales.
Assets Examples: Companies
A company lists its assets with a dollar amount on balance sheets. Assets are made up of liabilities and equity on the balance sheet. Common asset categories include:
Current Assets:
Cash and cash equivalents
Short term investments
Prepaid expense
Fixed assets:
Property and equipment
Accumulated Depreciation
Intangibles:
Trademarks, patents, etc.
Goodwill
Deferred tax asset
Investments and others
Long-term investments
Leased assets
Other assets
Every company needs assets to operate. For example, inventory might be sold for cash in order to cover operating expenses.
Assets Examples: Individuals
Individuals might not keep balance sheets for their finances. They should, however, keep a budget or some kind of organized financial record to determine their net worth. The net worth formula subtracts all liabilities (debt) from all assets.
Examples of individual assets include:
- Property/Homes
- Jewelry/Collectibles
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Certificates of deposit (CDs)
- Investments including bonds, mutual funds, and retirement plans
An investor’s portfolio is a collection of assets. It is widely believed that an individual's portfolio should include assets from several different categories, a practice called asset allocation. A simple example of asset allocation is holding a mixture of stocks, bonds, and cash.
Related Reading: 4 Steps to a Perfectly Balanced Portfolio
Types of Assets
Assets are broken into categories based on liquidity and function. On the balance sheet, they’re presented according to whether the asset will (or can) be used up within the next 12 months.
Liquid Assets
Liquid assets are either cash (on hand) or those that can be quickly converted to cash. One example of liquid assets is cash that’s held in a checking or savings account.
Current Assets
Current assets are expected to be consumed or converted into cash within one year. These fund day-to-day operations at a company. Examples of current assets include cash, short-term investments, inventory, and accounts receivable (also known as the expected payments from customers for goods or services performed).
Fixed Assets
Fixed assets (also known as long-term assets) are expected to be consumed or converted into cash after one year's time. You can find fixed assets beneath current assets on the balance sheet. Fixed assets like property (e.g. office space, buildings, equipment) are important because they support the operation of a business over the long term.
Tangible vs Intangible Assets
Assets are categorized by function/form. A tangible asset has a physical form (e.g. buildings equipment) while intangible assets do not (e.g. patents, trademarks, copyrights). A company’s assets are made up of a combination of tangible and intangible assets.
However, an asset must be able to be measured reliably. That’s why 'goodwill' is normally not included on a company balance sheet (except in the case of an acquisition or merger).
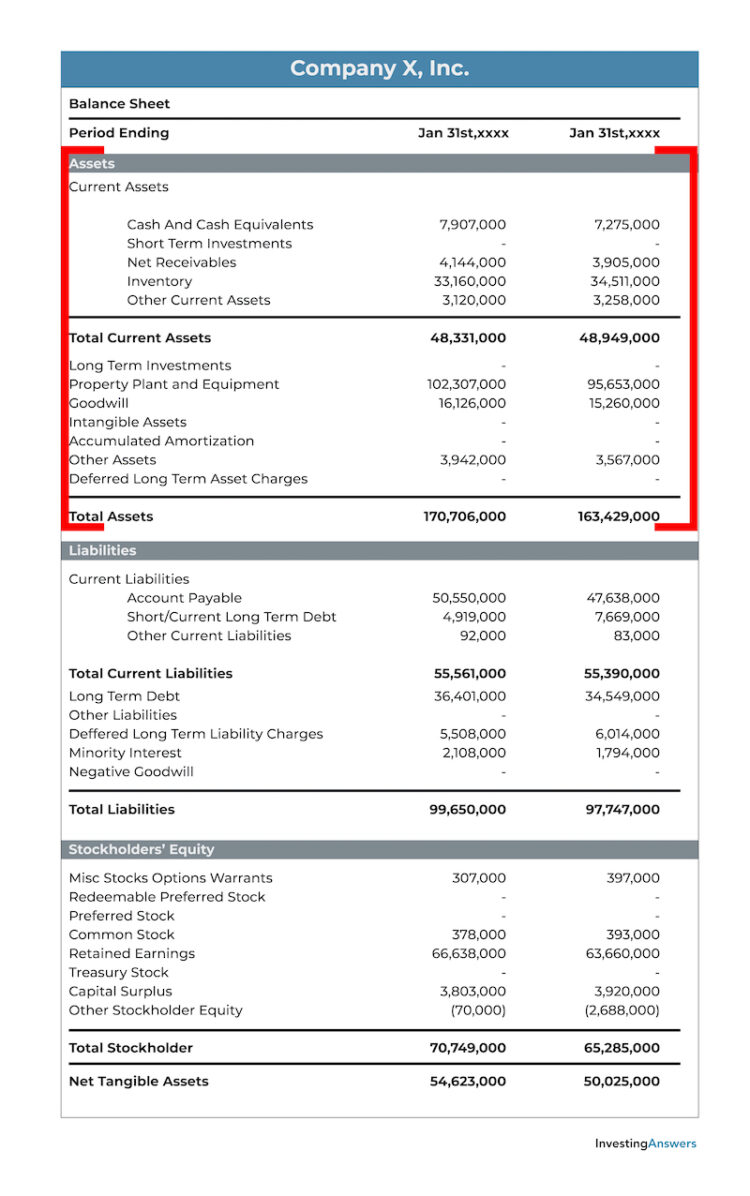
How Are Assets Listed on the Balance Sheet?
Below is an example of assets listed on a company balance sheet for Wal-Mart.
What Is an Asset Bubble?
An asset’s bubble occurs when its value rises dramatically within a short period of time. For instance, when investors buy an asset and rapidly increase the price beyond its actual value. This price isn’t supported by a product’s value and, eventually, the bubble bursts as demand falls and prices crash.
A great example of this is the Dutch Tulip Bubble (1636-37). When certain bulbs with a virus produced flowers with spectacular and unique color combinations, there was a massive boom in tulip future trading*. Owning these tulips was considered a status symbol, which drove prices up quickly – but the bulbs themselves weren’t worth this price increase. Within a year, the futures were due but the prices had dropped considerably.
*Future trading is a contract where the buyer agrees to pay a certain price for a defined asset at some future date. Futures trading is the trading of such contracts.
What Is Asset Management?
Assets create or preserve wealth, making them incredibly important to both individuals and companies. There are two asset management definitions:
- Company asset management ensures that all tangible and intangible assets are maintained and continue to provide value to the company.
- Asset management may be a service provided by a firm or company to help maintain and/or grow the investor’s assets. Financial institutions and banks offer asset management in order to make important investment decisions on behalf of their clients.
You should know how much value your assets provide. If managed well, assets can be used to increase your net worth or a company’s overall value.




