What is a J Curve?
The J curve represents a hypothetical short-term increase in a country's trade deficit that occurs immediately following a decline in the value of its currency.
How Does a J Curve Work?
When a country experiences a sustained decline in the value of its currency relative to its trading partners, its import volume (goods and services purchased from outside countries) temporarily exceeds its export volume (goods and services sold to outside countries). The country's export volume gradually corrects itself as the decline in the country's currency makes its goods and services cheaper for its trading partners.
Expressed on a graph with time on the horizontal axis and trade balance on the vertical axis, this phenomenon resembles the letter 'J'.
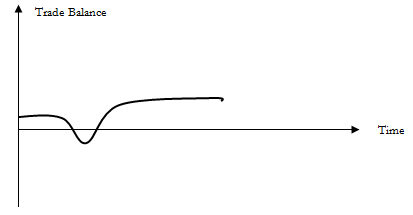
Why Does a J Curve Matter?
A J curve predicts that a country will eventually move to a trade surplus after its currency declines in value. As a result, the country will eventually see positive net income from trade.



