What Is Gross Profit?
Also referred to as gross income or sales profit, gross profit is the total sales of a company minus the total cost of goods (COGS) sold. Gross profit reports are an important indicator of a company’s profitability.
How to Calculate Gross Profit
While you can typically find gross profit on an income statement, it’s possible to solve for the difference between the cost of goods sold and total sales (aka revenue).
Let’s break down the components of the gross profit formula:
1. Find the Total Sales
Total sales (e.g. revenue) can be found by adding up all of the goods sold within a specific period of time, such as annually or quarterly.
2. Find the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
When calculating COGS, only variable costs (ie. expenses that change depending on the quantity of product being produced) are included. For example, in a car factory, variable costs may include:
- Raw materials such as steel, plastic, and glass
- Electricity bills and utilities for the factory
- Assembly line labor wages
COGS Doesn't Include Fixed Costs
It's important to remember that COGS doesn’t include fixed costs (ie. expenses involved with the general upkeep of the business). In a car factory, these fixed costs might include:
- Insurance
- Rent, and
- Routine maintenance.
How to Use the Gross Profit Formula
The gross profit formula is expressed as follows:

Gross Profit Example
Consider the example of a modified income statement from Car Manufacturer XYZ.
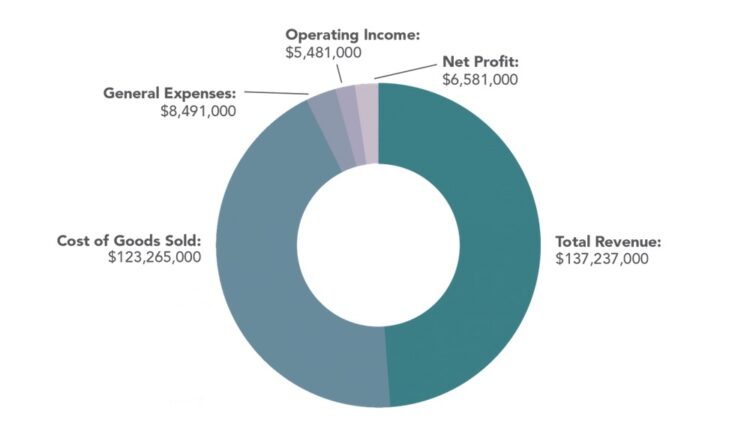
Car Manufacturer XYZ had a total revenue of $137,237,000 last year and production and distribution of its goods (COGS) was $123,265,000.
We can calculate Car Manufacturer XYZ’s gross profit by taking its overall revenue and subtracting cost of goods sold:
$137,237,000 − $123,265,00 = $13,972,000
Therefore, last year, Car Manufacturer XYZ had a gross profit of $13,927,000.
Net Profit vs Gross Profit
Gross profit reveals how much revenue a business has after considering the costs of production. Gross profit is important because it allows us to calculate other key financial metrics like gross profit margin.
Why Is Gross Profit Important?
Gross profit reveals how much revenue a business has after considering the costs of production.
On its own, gross profit doesn’t tell analysts or investors much about a business’ performance, and only looking at a company’s gross profit (as an indicator of profitability over time) can be deceptive and dangerous.
Note: Gross profit figures can rise even as a company’s gross profit margins decrease, which would indicate a drop in profitability.
How Gross Profit Is Different Than Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit allows you to easily find the gross profit margin, which is an indicator of company profitability. It shows the gross profit as a percentage of sales.
What Gross Profit Margin Tells Us
A high gross profit margin suggests a business that is efficient at generating sales in excess of the costs of the goods sold (ie. one that’s more efficient at utilizing resources). Investors and analysts are able to use gross profit margin to either track a business’s performance over time or compare a company to its industry competitors.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin
To calculate gross profit margin, divide gross profit by total revenue. The gross profit margin formula can be expressed as follows:
Gross Profit Margin % = Gross Profit/ Total Sales Revenue
Gross Profit Margin Example
Using the Car Manufacturer XYZ’s income statement above, we can compute gross profit margin by dividing its gross profit by its total revenue. This would look like:
($13,927,000 / $137,237,000) x 100 = 10.15%
Let’s look at another calculation for competing Car Manufacturer ABC. The competitor had total revenue of $120,207,000 and gross profit of $10,515,000 in 2019. Using the above formula the gross profit margin is 8.75%:
$10,515,000/$120,207,000)x 100 =8.75%
If both companies are in the same industry, it’s easy to compare the gross profit margins to determine which company is performing more efficiently.
Because Car Manufacturer XYZ has a slightly higher gross profit margin, we can infer that it is more efficient at converting raw materials and labor into revenue. This suggests Car Manufacturer XYZ has more of its funds to direct towards savings, operations, and indirect expenses. Between the two companies, Car Manufacturer XYZ has a greater earning potential overall.
Limitations of Using Gross Profit Margin as a Metric
When viewed alone, gross profit margin can be misleading to assess a company’s profitability or future earnings potential. Gross profit margin only considers production costs and doesn’t include costs such as taxes, marketing, and rent. Because of this, gross profit margin is not always the most accurate measure of profitability and should be used in conjunction with other metrics.
For example, Car Manufacturer XYZ’s gross profit margin could be increasing, but if taxes, rent, and other costs rise even faster, the company may not be adapting to changing market conditions (and may be mismanaged).




