Recently, homebuyers have enjoyed historically low mortgage rates. Although this dip in mortgage rates is helpful to potential homebuyers, historical mortgage rates have affected the real estate market for decades.
Historical mortgage rates have made their mark on homebuyer's budgets. Let's explore how historical mortgage rates have changed over time. Plus, how these rates can affect home prices.
Historical Mortgage Rates 1971 to 2021
Freddie Mac started to record historical mortgage rates through lender surveys in 1971. Since that point, 30-year mortgage rates have been recorded as they rose to record highs and fell to record lows in the intervening decades.
In the early 1970s, the rates for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages hovered around the 7% mark. By the late 1970s, high inflation had taken hold in the economy. With that, the Federal Reserve chose to increase the federal funds rate. Mortgage rates continued to rise towards the historic peak of 18.83% in 1981.
Since the historic peak, consumers have seen some fluctuation. However, the extremely dramatic increase in rates seen in the early years of tracking hasn't been repeated on record.
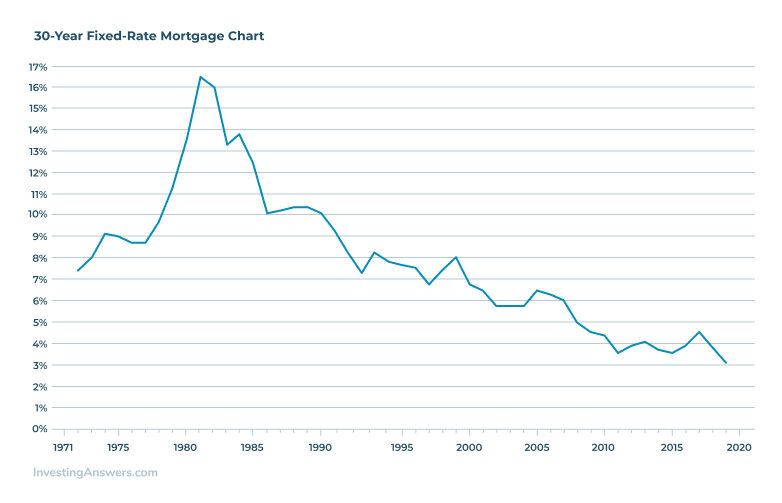
Mortgage Rates Charts
Let's take a closer look at the data to visualize historical mortgage rates better.
15-Year vs. 30-Year Rates
Although Freddie Mac began to record interest rates for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages in 1971, the organization did not start recording the same information for 15-year fixed-rate mortgages until 1991. With that, the table below shows a comparison between historical mortgage rates for 15-year and 30-year mortgages.
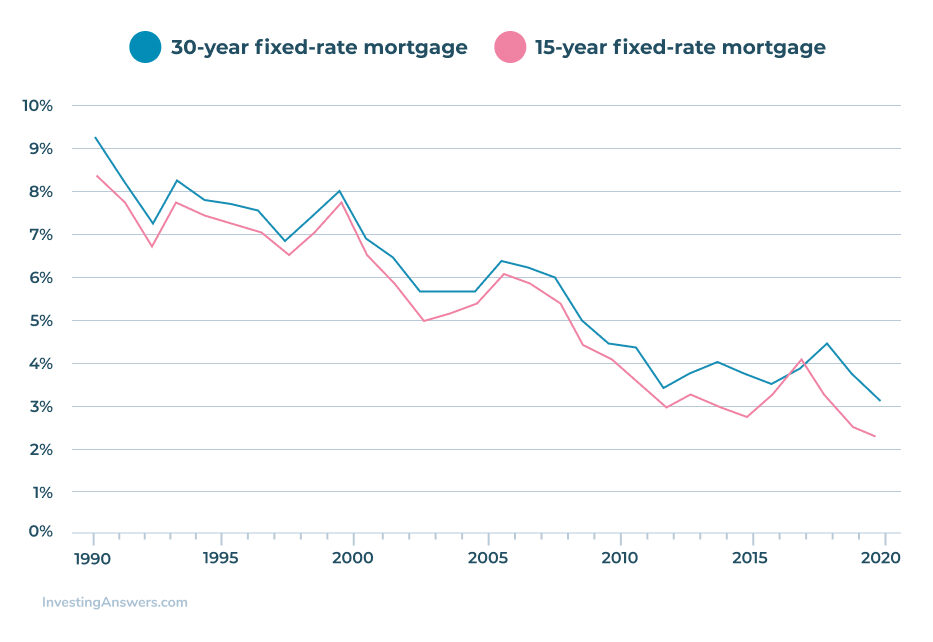
Based on the data made available by Freddie Mac, the interest rates of 30-year fixed mortgages are always higher than 15-year interest rates. Many homebuyers choose to lock in a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage even with the slightly higher interest rate. The longer-term means a lower monthly payment, which is attractive to many buyers.
The lower rates offered through 15-year mortgages can make it possible to save in interest payments over the lifetime of the loan. But the shorter term means a higher payment. And many homebuyers are unable to fit the larger monthly payment into their budget.
Adjustable Rates vs. 30-year Rates
Freddie Mac began to record the average interest rates for 5-year Adjustable-Rate Mortgages in 2005. With that, the table below reflects a comparison between 30-year fixed-rate mortgage rates and 5-year Adjustable-Rate mortgages with a 30-year term starting in 2005.
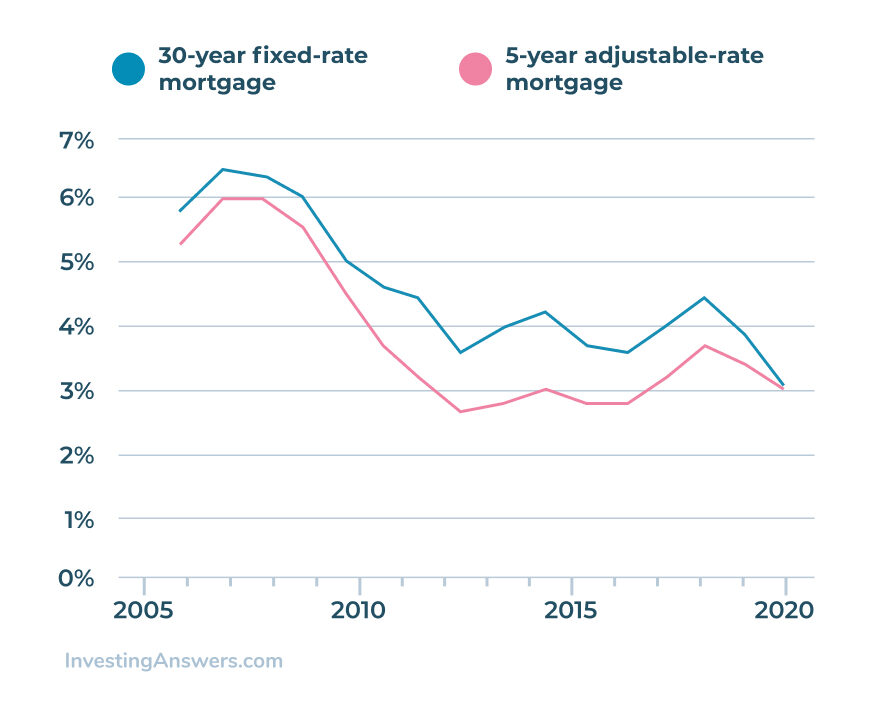
Adjustable-rate mortgages can provide the opportunity to save money on interest in the short term. However, rate fluctuations can make it difficult to budget for your future mortgage payment beyond the first five years.
What is the Highest Mortgage Rate in History?
The highest recorded mortgage rate for 30-year fixed-rate mortgages was 18.45%. Freddie Mac recorded this new height in 1981. More recently, the lowest average mortgage rate in history was recorded at 2.68% in 2020.
To put these numbers into context, the monthly mortgage payment for a $100,000 loan at the peak mortgage rates for a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage in 1981 was $1,544. In contrast, the monthly mortgage payment for a $100,000 loan at the recent low of 2.68% is $405.
The difference between these two interest rates could make or break a homebuyer's dreams.
How Mortgage Rates Affect Home Prices
As historical mortgage rates have swung back and forth, homebuyers have been forced to face the consequences. Not only do changing interest rates have an impact on monthly budgets, but also the number of potential home shoppers.
In many instances, low interest rates have caused an increase in home buyers because homes become more affordable. With an increase in interested buyers, the demand typically tends to push home prices higher. However, it is important to note that this general correlation doesn't always appear based on unique economic circumstances.
For example, during the Great Recession, there was a period of time when interest rates and prices fell in tandem. With the numerous factors affecting home prices, mortgage rates are not the only piece of the puzzle.
With dropping interest rates throughout 2020, the real estate market saw a dramatic rise in home prices. As mortgage rates fell, buyers were able to fit a larger mortgage into their monthly budget. In fact, the median home price rose from $270,400 in February 2020 to $313,000 in February 2021.
Let's consider how a potential home buyer with a monthly budget of $1,500 would be affected by changing interest rates. With a fixed-rate of 3% on a 30-year mortgage, this homebuyer could afford a $355,000 home. But if the interest rates rose to 6%, the same buyer would only be able to afford a $250,000 home. It is clear to see that changing interest rates can have a big impact on your home shopping budget.



