What is the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD)?
The Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) is an international economic forum that pursues cooperative approaches to common issues affecting individual members as well as the global community.
How Does the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Work?
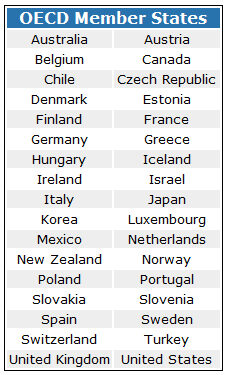
The OECD was formed in 1948 as part of the plan to rebuild Europe following the Second World War, known as the Marshall Plan. The OECD comprises delegations from numerous market economies. Member states include:
To illustrate the how the OECD may work in the global market, suppose Country XYZ, a large exporter of grain, has experienced a severe drought in recent months. Consequently, the importers who rely on Country XYZ's grain have been experiencing food shortages. The OECD is likely to hold discussions about how these food shortages are affecting member countries and suggest possible approaches to remedy the situation.
Why Does the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Matter?
The OECD is instrumental in keeping lines of communication open between the world's capitalist economies. Through cooperative discussion, OECD members try to improve economic hardships through an exchange of ideas. In recent years, this has become more important with the removal of trade barriers and increased economic interdependence among national economies.



